Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokoyama, Sumi; Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Iida, Takao*; Furuichi, Shinya*; Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*; Kaneto, Taihei*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 116(1-4), p.401 - 405, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.41(Environmental Sciences)The physicochemical property of radionuclides suspended in the air is an important parameter to evaluate internal doses due to the inhalation of the airborne radionuclides and to develop the air monitoring system in high-energy proton accelerator facilities. This study focuses on the property of radioactive airborne chlorine ( Cl and
Cl and 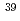 Cl) and sulfur (
Cl) and sulfur ( S) formed from Ar gas by irradiation with high-energy neutrons. As a result of the irradiation to a mixture of Ar gas and dry air,
S) formed from Ar gas by irradiation with high-energy neutrons. As a result of the irradiation to a mixture of Ar gas and dry air,  Cl and
Cl and 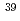 Cl existed as non-acidic gas and
Cl existed as non-acidic gas and  S was present as acidic gas. Further, it was found that in the high-energy neutron irradiation to aerosol containing-Ar gas, the higher the amount of radioactive aerosols becomes, the lower that of radioactive acidic gas becomes.
S was present as acidic gas. Further, it was found that in the high-energy neutron irradiation to aerosol containing-Ar gas, the higher the amount of radioactive aerosols becomes, the lower that of radioactive acidic gas becomes.
Nakashima, Hiroshi; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Masukawa, Fumihiro; Matsuda, Norihiro; Oguri, Tomomi*; Nakano, Hideo*; Sasamoto, Nobuo*; Shibata, Tokushi*; Suzuki, Takenori*; Miura, Taichi*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 115(1-4), p.564 - 568, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.02(Environmental Sciences)The High Intensity Proton Accelerator Project, named as J-PARC, is in progress, aiming at studies on the latest basic science and the advancing nuclear technology. In the project, the high-energy proton accelerator complex of the world highest intensity is under construction. In order to establish a reasonable shielding design, both simplified and detailed design methods were used in the shielding design of J-PARC. This paper reviews the present status of the radiation safety design study for J-PARC.
 H and
H and  C induced in concrete shielding of an electron accelerator facility
C induced in concrete shielding of an electron accelerator facilityEndo, Akira; Harada, Yasunori; Kawasaki, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masamitsu
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 60(6), p.955 - 958, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.06(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Endo, Akira; Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Iida, Takao*; Furuichi, Shinya*; Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 256(2), p.231 - 237, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.77(Chemistry, Analytical)Size distributions of  Cl,
Cl, 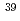 Cl,
Cl, 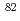 Br and
Br and 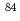 Br aerosols generated by irradiations of argon and krypton gases containing di-octyl phthalate (DOP) aerosols with 45MeV and 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were measured to study the formation mechanism of radioactive particles in high energy radiation fields. Effects of the size distribution of the radioactive aerosols on the size of added DOP aerosols, the energy of irradiation neutrons and the kinds of nuclides were studied. The observed size distributions of the radioactive particles were explained by attachment of the radioactive atoms generated by the neutron-induced reactions to the DOP aerosols.
Br aerosols generated by irradiations of argon and krypton gases containing di-octyl phthalate (DOP) aerosols with 45MeV and 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were measured to study the formation mechanism of radioactive particles in high energy radiation fields. Effects of the size distribution of the radioactive aerosols on the size of added DOP aerosols, the energy of irradiation neutrons and the kinds of nuclides were studied. The observed size distributions of the radioactive particles were explained by attachment of the radioactive atoms generated by the neutron-induced reactions to the DOP aerosols.
Yoshizawa, Michio; Endo, Akira
JAERI-Conf 2003-002, 166 Pages, 2003/03
The present report is Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Dosimetry for External Radiations, held at the Tokai Research Establishment, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), in November 28-29, 2002. The proceedings comprises 16 papers and a summary of general discussion. The Third Workshop, subtitled "On an opportunity of the completion of the facility of calibration standards for neutron at JAERI", focused on neutron dosimetry and included presentations on the status of international neutron standards, the development of calibration techniques of neutron dosimeters using accelerator neutron sources, and dosimetry for high-energy neutrons. The workshop identified the directions for the future research and development in this field.
Miyamoto, Yukihiro; Ikeno, Koichi; Akiyama, Shigenori*; Harada, Yasunori
JAERI-Tech 2002-086, 43 Pages, 2002/11
Description is given for the characteristic radiation environment for the High Intensity Proton Accelerator Facility and the design concept of the radiation control system of it. The facility is a large scale accelerator complex consisting of high energy proton accelerators carrying the highest beam intensity in the world and the related experimental facilities and therefore provides various issues relevant to the radiation environment. The present report describes the specifications for the radiation control system for the facility, determined in consideration of these characteristics.
Endo, Akira; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*; Iida, Takao*; Sato, Kaoru; Tsuda, Shuichi
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 56(4), p.615 - 620, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.39(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Formation mechanism and size distribution of radioactive aerosol particles generated in a high-energy neutron field were studied in order to evaluate a particle size parameter for internal dose evaluation in high-energy accelerator facilities. Argon gas containing DOP aerosols was irradiated by a 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutron beam of TIARA. The number size distribution of the DOP aerosols and the activity-weighted size distribution of  Cl and
Cl and 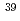 Cl aerosols, formed from the (n, 2np) and (n, np) reactions of
Cl aerosols, formed from the (n, 2np) and (n, np) reactions of  Ar, were measured using an electrical low-pressure impactor. The activity-weighted size distribution of the radioactive aerosols was well explained by the simple attachment model of the radioactive atoms to the DOP aerosols.
Ar, were measured using an electrical low-pressure impactor. The activity-weighted size distribution of the radioactive aerosols was well explained by the simple attachment model of the radioactive atoms to the DOP aerosols.
 C produced in the air in high energy proton accelerator tunnels
C produced in the air in high energy proton accelerator tunnelsEndo, Akira; Oki, Yuichi*; Kanda, Yukio*; Oishi, Tetsuya; Kondo, Kenjiro*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 93(3), p.223 - 230, 2001/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.06(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; ; Watanabe, Hiromasa; Yamano, Naoki*
JAERI-Data/Code 97-019, 91 Pages, 1997/05
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Tatsuo; Ono, Hideo; R.A.Jameson*; J.A.Hassberger*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 22, p.117 - 127, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:55.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English